


Received: 04-Feb-2022, Manuscript No. GJAEE-22-63286; Editor assigned: 09-Feb-2022, Pre QC No. GJAEE-22-63286(PQ); Reviewed: 23-Feb-2022, QC No. GJAEE-22-63286; Revised: 02-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. GJAEE-22-63286(R); Published: 10-Mar-2022, DOI: 10.15651/GJAEE.22.10.04
Agriculture and farming are the customs of growing crops and livestock. Agriculture has been an important development in the rise of sedentary human civilization and domesticated species of agriculture have created food surpluses that allow people to live in cities. The history of agriculture began thousands of years ago. After collecting wild crops that started at least 105,000 years ago, aspiring farmers began planting them about 11,500 years ago. Pigs, sheep and cattle were domesticated over 10,000 years ago. The plants are grown independently in at least 11 regions of the world. In the 20th century, large-scale monoculture-based industrial agriculture dominated agricultural production, but about 2 billion people were still dependent on subsistence agriculture. Modern agriculture, plant breeding, pesticides such as pesticides and fertilizers, and technological developments have significantly increased crop yields, but have caused environmental and damage. Breeding is modern livestock practices have increased meat product as well, but have raised concerns about animal welfare and environmental damage. agriculture and farming are damaged.
In civilization Eurasia, the summers began around 8,000 BC. Living in a village, relying on the Tigris-Euphrates and the canal system for irrigation plows appear in pictograms around 3000 BC. Seed plow circa 2300 BC Farmers cultivated vegetables such as wheat, barley, lentils and onions, and fruits such as dates, grapes and figs. Ancient Egyptian agriculture relied on the Nile and its seasonal floods. Agriculture began at the end of the Paleolithic period, in the pre-dynasty period after 10,000 BC. The staple food was grains such as wheat and barley, along with industrial crops such as flax and papyrus. Wheat, barley and jujube were cultivated in India around 9,000 BC. Domesticated, soon followed by sheep and goats. In the Americas, pumpkin, beans and cocoa are one of the crops cultivated in Mesoamerica (excluding Theosinte). Cacao was domesticated by Mayo Chinchipe in the upper Amazon River around 3,000 BC. Turkey was probably domesticated in Mexico or the American Southwest .The Aztecs developed irrigation systems, formed terraced hillsides, fertilized their soil and developed chinampas or artificial islands. The Mayas used extensive canal and raised field systems to farm swampland from 400 BC. Coca was domesticated in the Andes, as were the peanut, tomato, tobacco and pineapple. Cotton was domesticated in Peru by 3,600 BC. Animals including llamas, alpacas and guinea pigs were domesticated there .In North America, the indigenous people of the East domesticated crops such as sunflower, tobacco, squash and chenopodium wild foods including wild rice and maple sugar were harvested. The domesticated strawberry is a hybrid of a Chilean and a North American species, developed by breeding in Europe and North America.
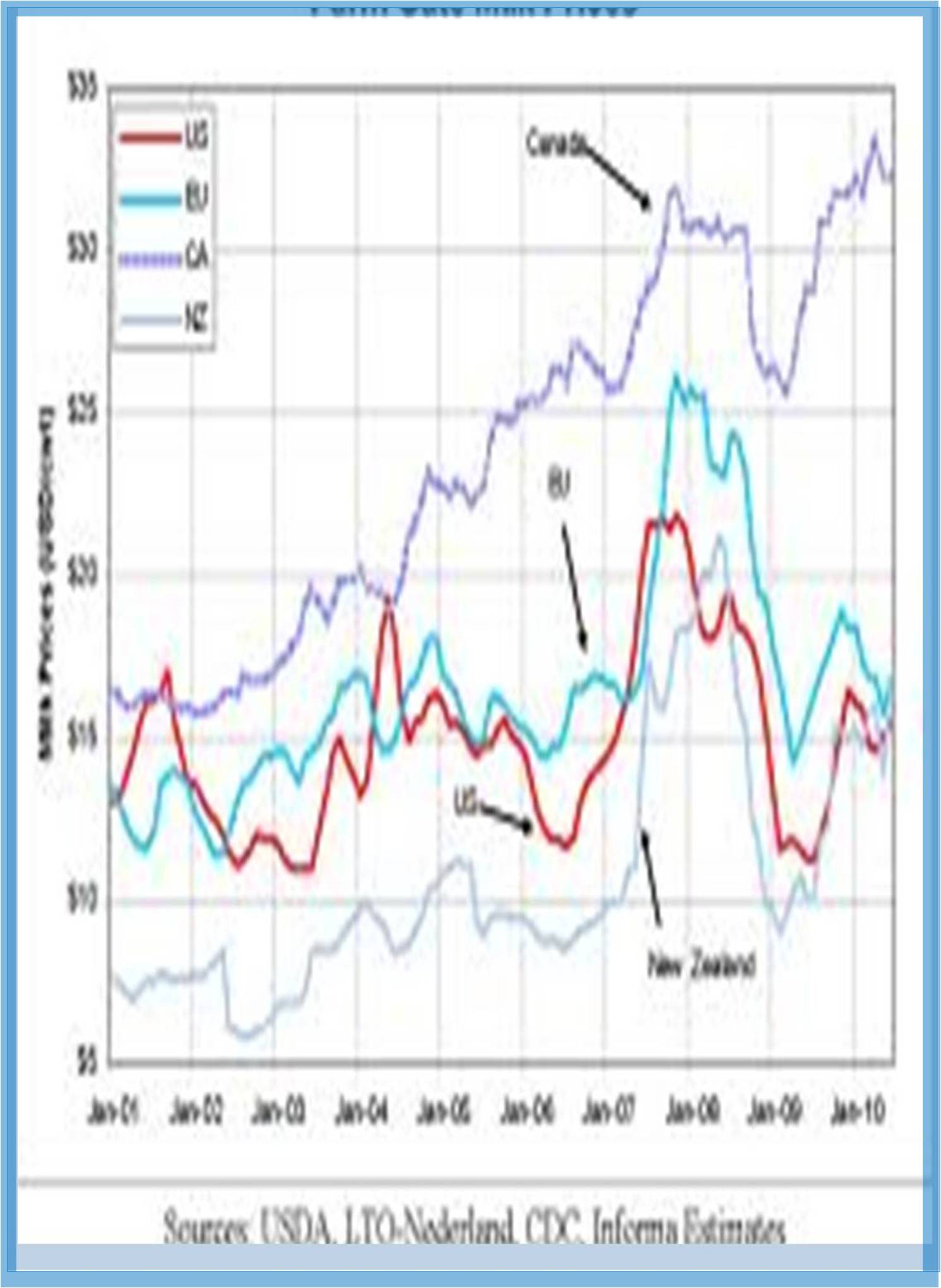
Environmental conditions: Environment agriculture in recent mainstream technological developments include genetically modified food demand for non food biofuel crops, development of former farm lands, rising transportation costs, climate change, growing consumer demand in China and India, and population growth, are threatening food security in many parts of the world. Accelerating climate change could further cut crop yields, especially in status from the twentieth century, intensive agriculture increased productivity. It substituted synthetic fertilizers and pesticides for labor, but caused increased water pollution, and often involved farm subsidies.
In recent years there has been a backlash against the environmental effects of conventional agriculture, resulting in the organic, regenerative and sustainable agriculture movements one of the major forces behind this movement has been the European Union, which first certified organic food in 1991 and began reform of its common agricultural policy in 2005 to phase out commodity linked farm subscribe also known as decoupling. The growth of organic farming has renewed research has renewed research in alternative technologies such as integrated pest management, selective breeding and controlled the world`s most food insecure regions.
Agriculture, forestry and land use changes are responsible for about 25% of greenhouse gas emissions. Agricultural mitigation is part of the climate change solution. A food system 2030 provides advice and analytical products to support policy options and provides innovative approaches and a means to test information to support change in situations in different countries. Work with the private sector by supporting the design, piloting and risk mitigation of innovative public-private partnerships that advance development and climate goals.